 Photo ©
Liz Clayton Fuller
Photo ©
Liz Clayton Fuller
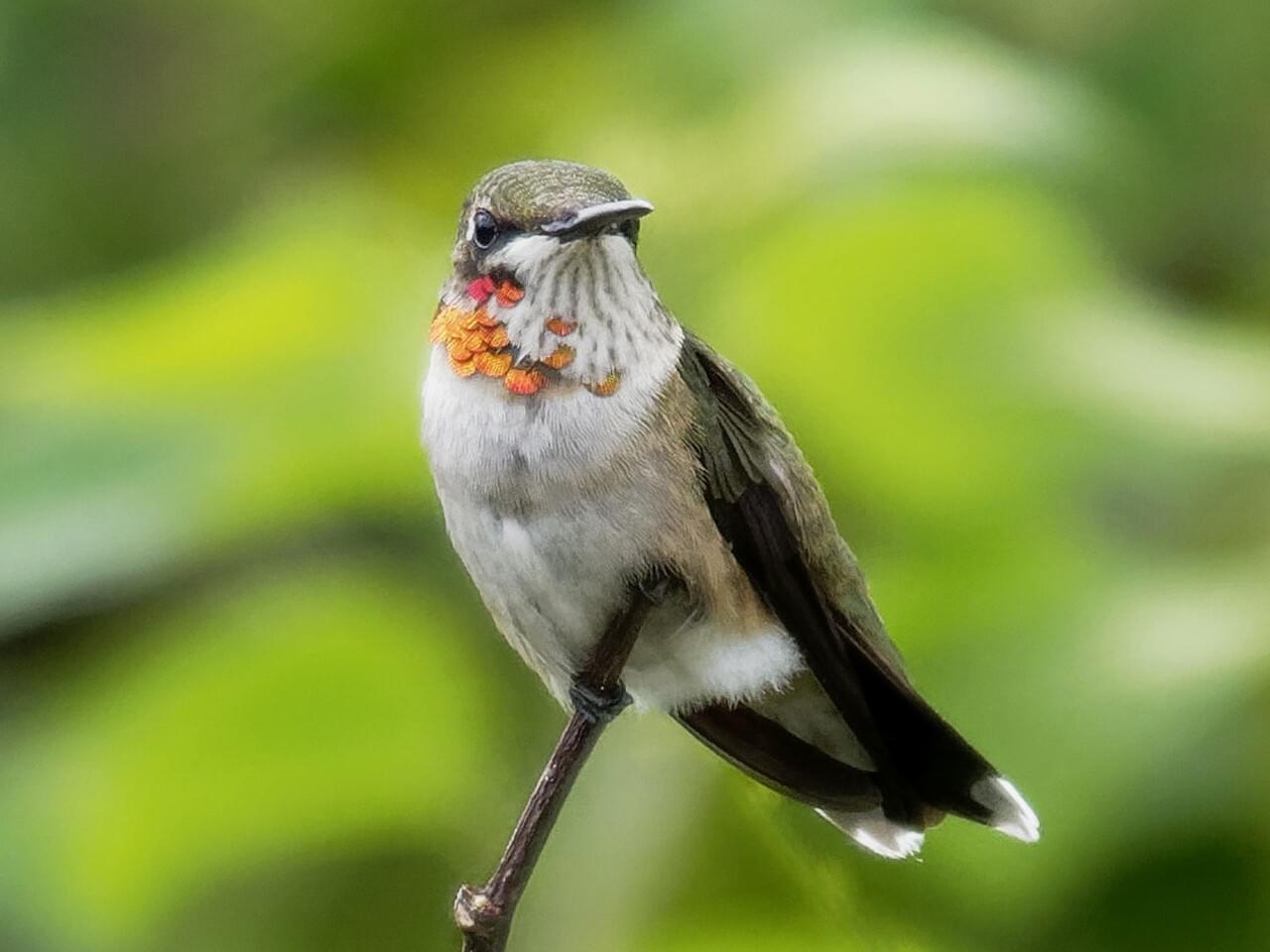
Ruby-throated Hummingbird
A flash of green and red, the Ruby-throated Hummingbird is eastern North America’s sole breeding hummingbird. These brilliant, tiny, precision-flying creatures glitter like jewels in the full sun, then vanish with a zip toward the next nectar source. Feeders and flower gardens are great ways to attract these birds, and some people turn their yards into buzzing clouds of hummingbirds each summer. Enjoy them while they’re around; by early fall they’re bound for Central America.
Range
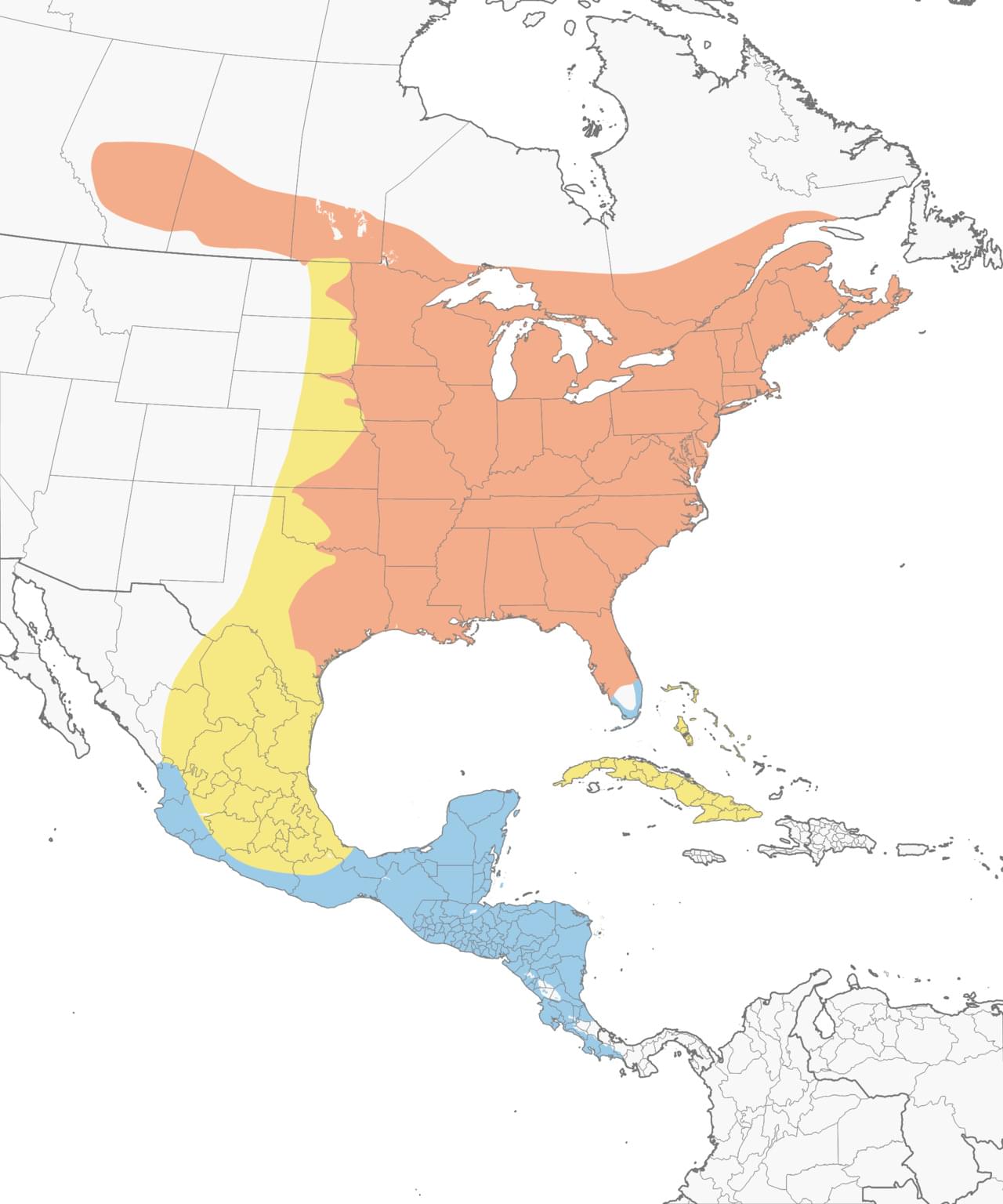
Habitat
Ruby-throated Hummingbirds occur in deciduous woodlands of eastern North America as well as across the Canadian prairies. Commonly associated with old fields, forest edges, meadows, orchards, stream borders, and backyards. On their tropical wintering grounds, Ruby-throated Hummingbirds live in dry forests, citrus groves, hedgerows, and scrub.
Food
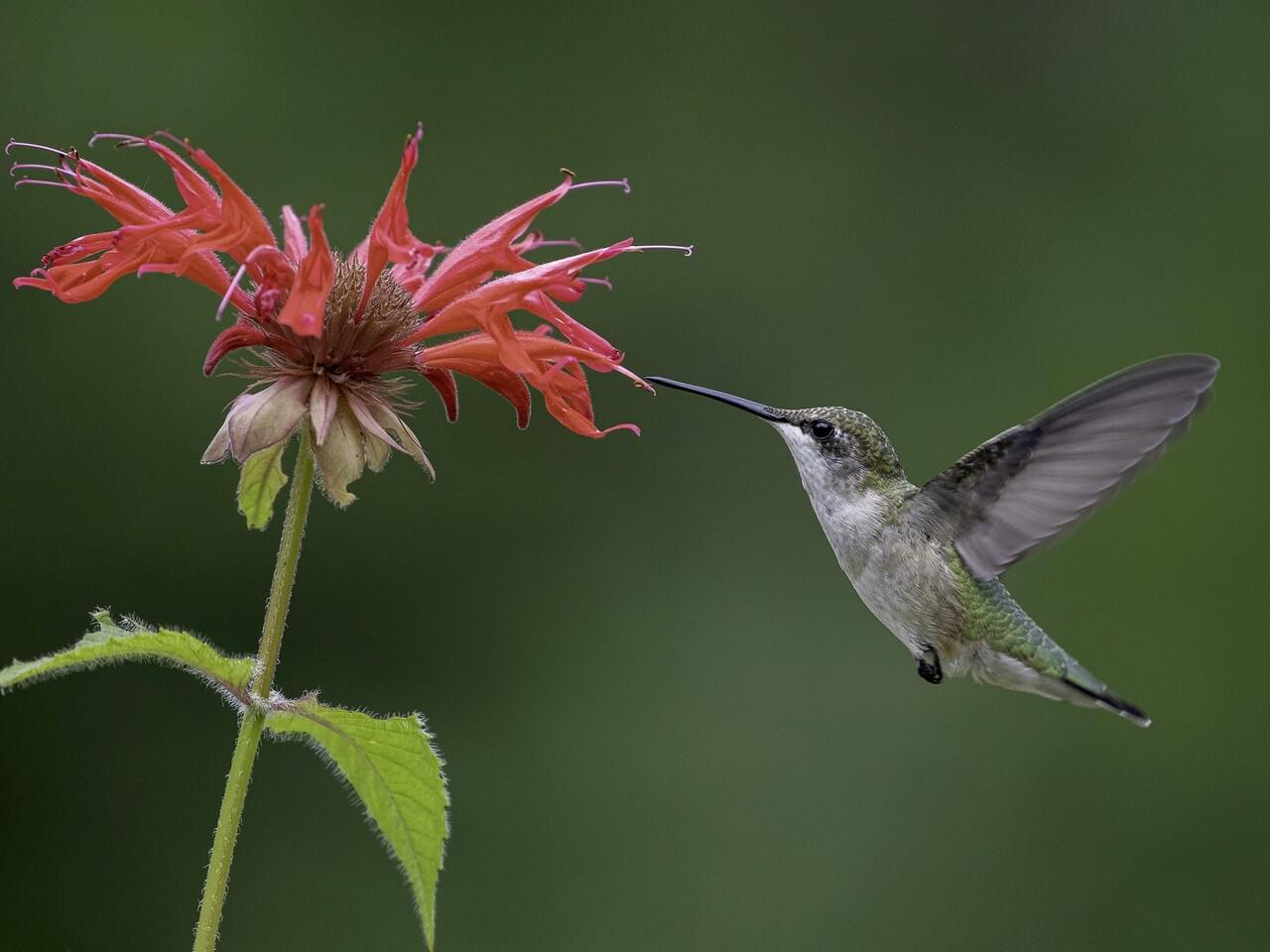
Ruby-throated Hummingbirds feed on the nectar of red or orange tubular flowers such as trumpet creeper, cardinal flower, honeysuckle, jewelweed, bee-balm, red buckeye and red morning glory, as well as at hummingbird feeders and, sometimes, tree sap. Hummingbirds also catch insects in midair or pull them out of spider webs. Main insect prey includes mosquitoes, gnats, fruit flies, and small bees; also eats spiders. Ruby-throated Hummingbirds sometimes take insects attracted to sap wells or picks small caterpillars and aphids from leaves.
Behavior
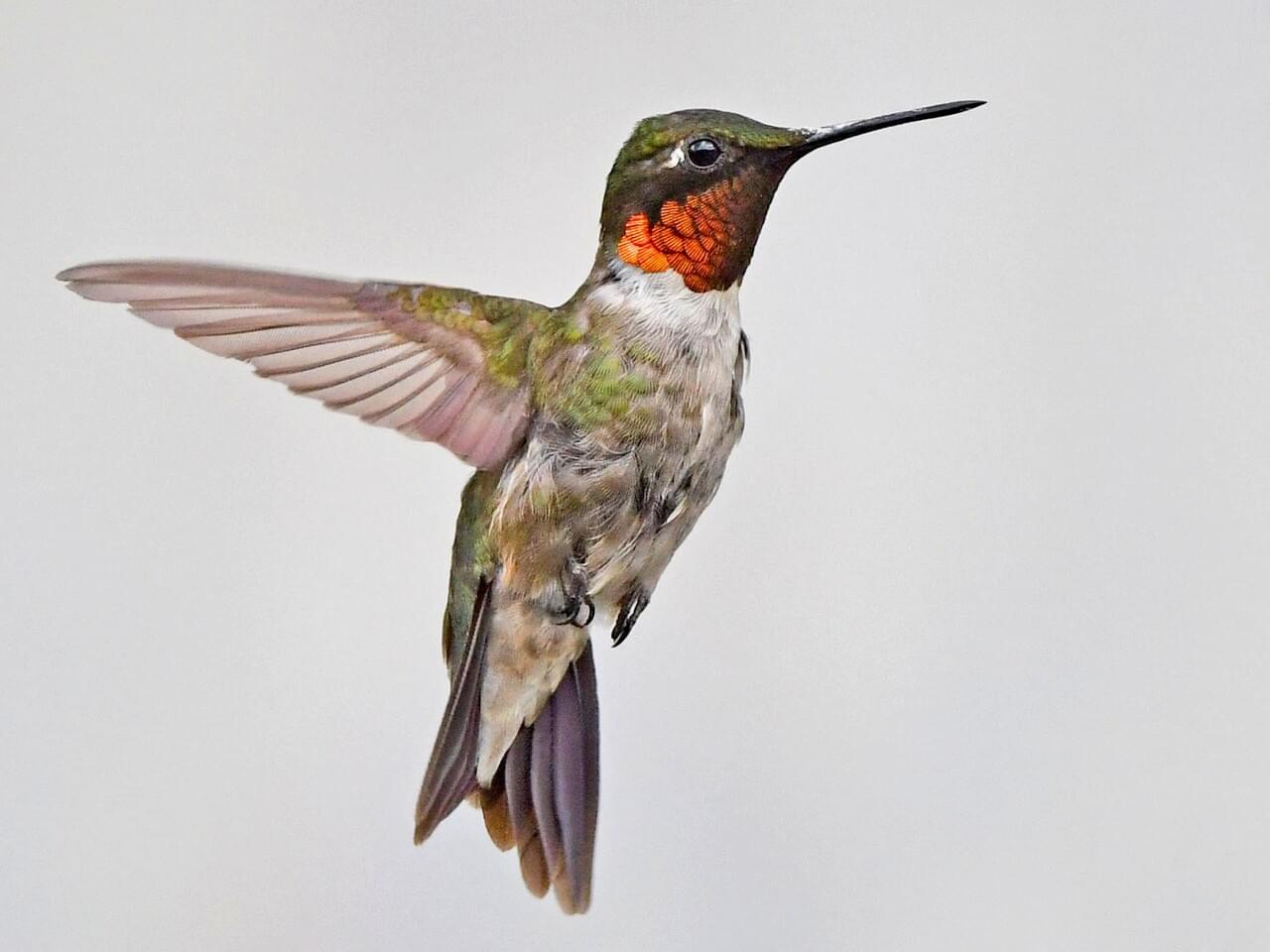
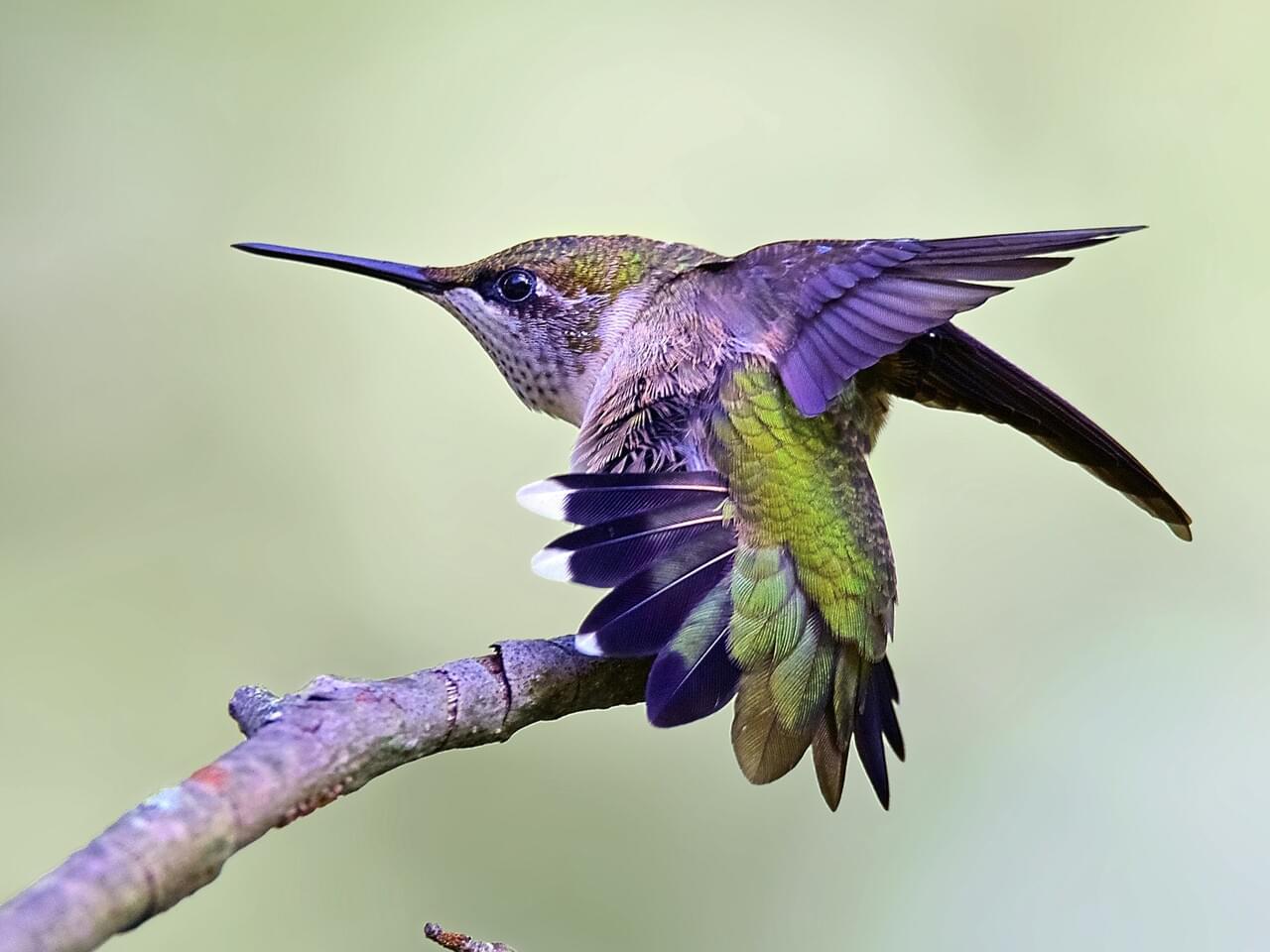
Like all hummingbirds, ruby-throats are precision flyers with the ability to fly full out and stop in an instant, hang motionless in midair, and adjust their position up, down, sideways, and backwards with minute control. They dart between nectar sources with fast, straight flights or sit on a small twig keeping a lookout, bill waving back and forth as the bird looks around. Male Ruby-throated Hummingbirds aggressively defend flowers and feeders, leading to spectacular chases and dogfights, and occasional jabs with the beak. They typically yield to larger hummingbird species (in Mexico) and to the notoriously aggressive Rufous Hummingbird. Males give a courtship display to females that enter their territory, making a looping, U-shaped dive starting from as high as 50 feet above the female. If the female perches, the male shifts to making fast side-to-side flights while facing her.
Nesting
The nest takes 6-10 days to finish and measures about 2 inches across and 1 inch deep with the inner cup about the size of a large thimble. The nest is built directly on top of the branch rather than in a fork. It’s made of thistle or dandelion down, held together with strands of spider silk and sometimes pine resin. The female stamps on the base of the nest to stiffen it, but the walls remain pliable, allowing it to stretch as the chicks grow. She shapes the rim of the nest by pressing and smoothing it between her neck and chest. The exterior of the nest is decorated (probably camouflaged) with bits of lichen and moss.
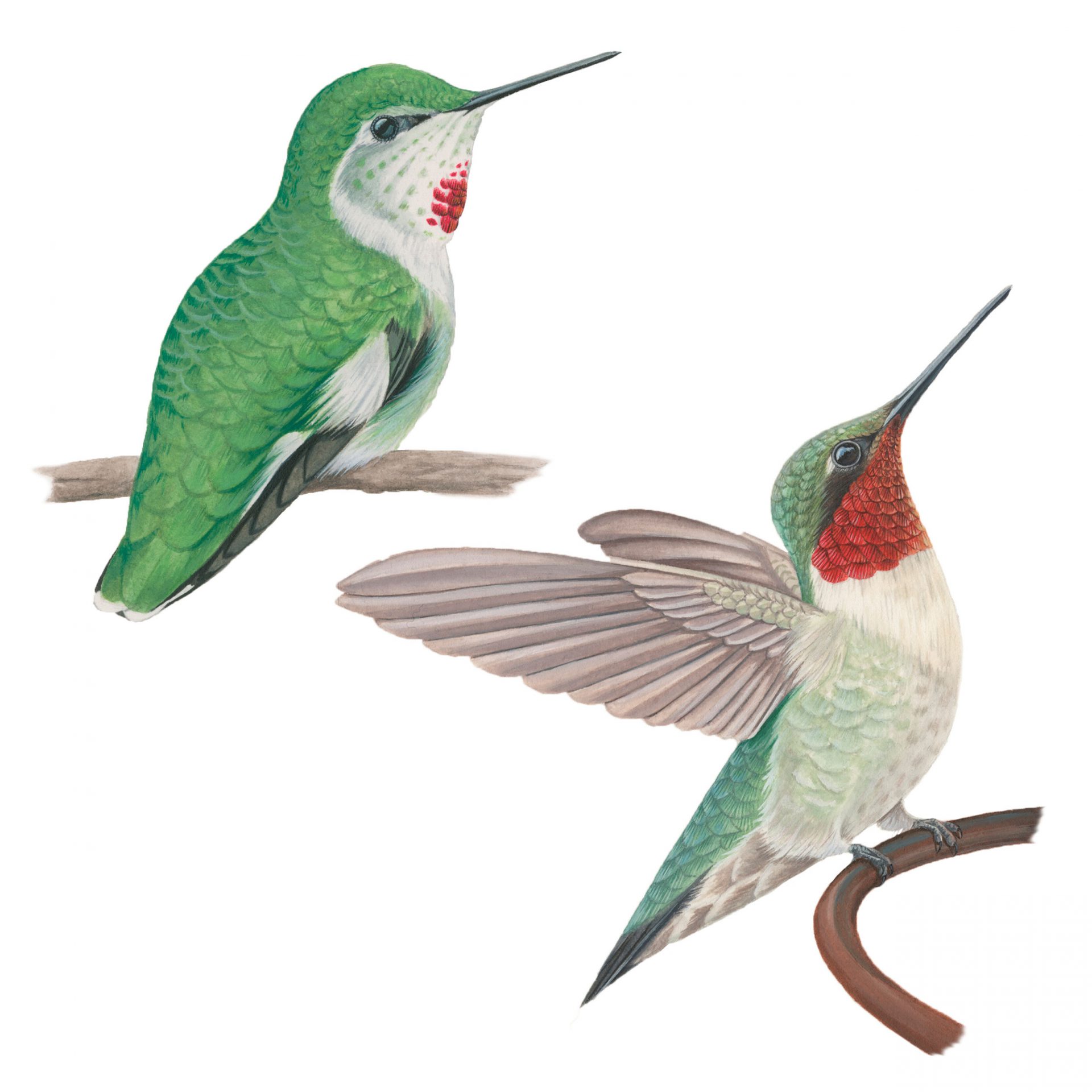
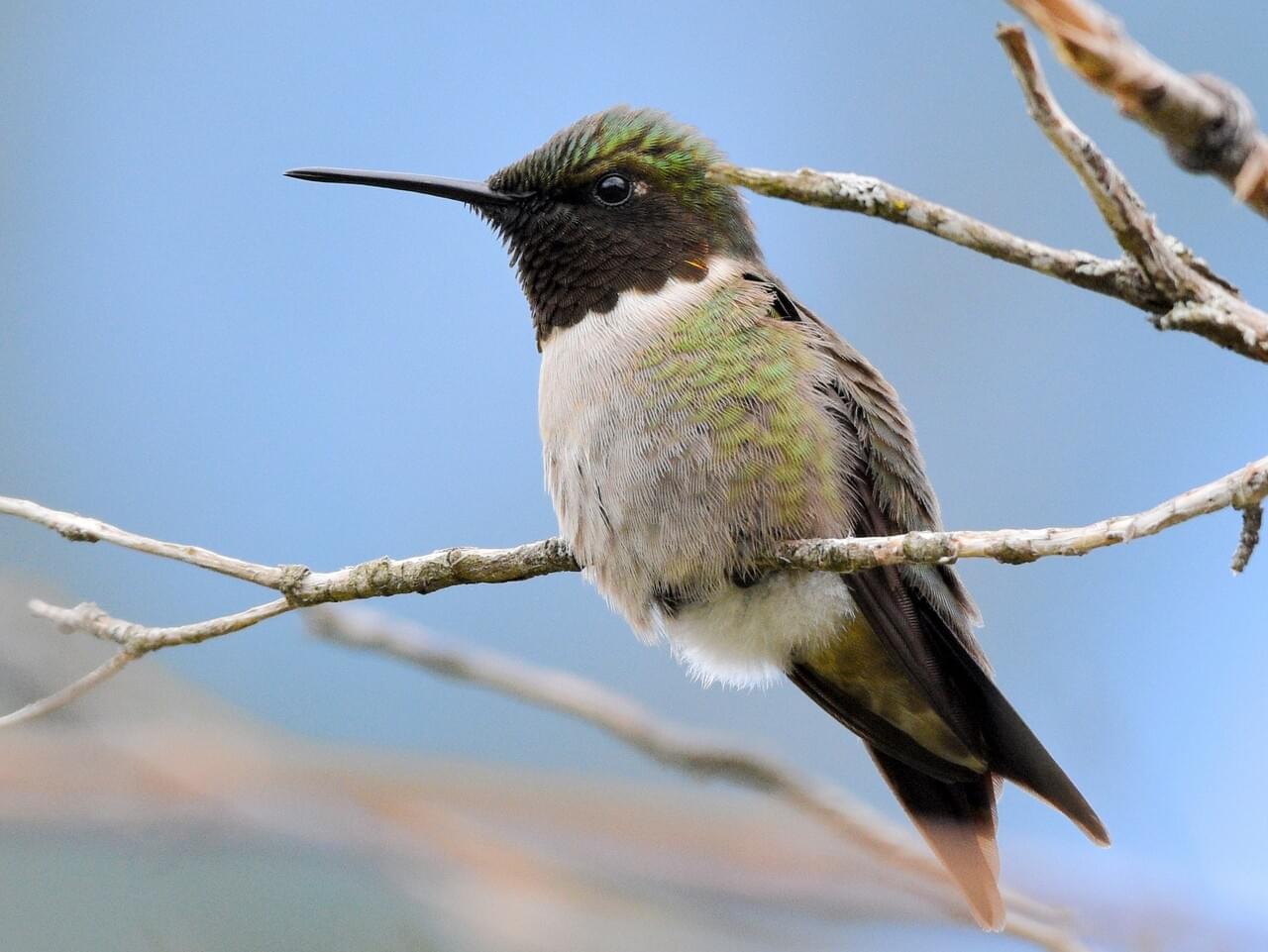
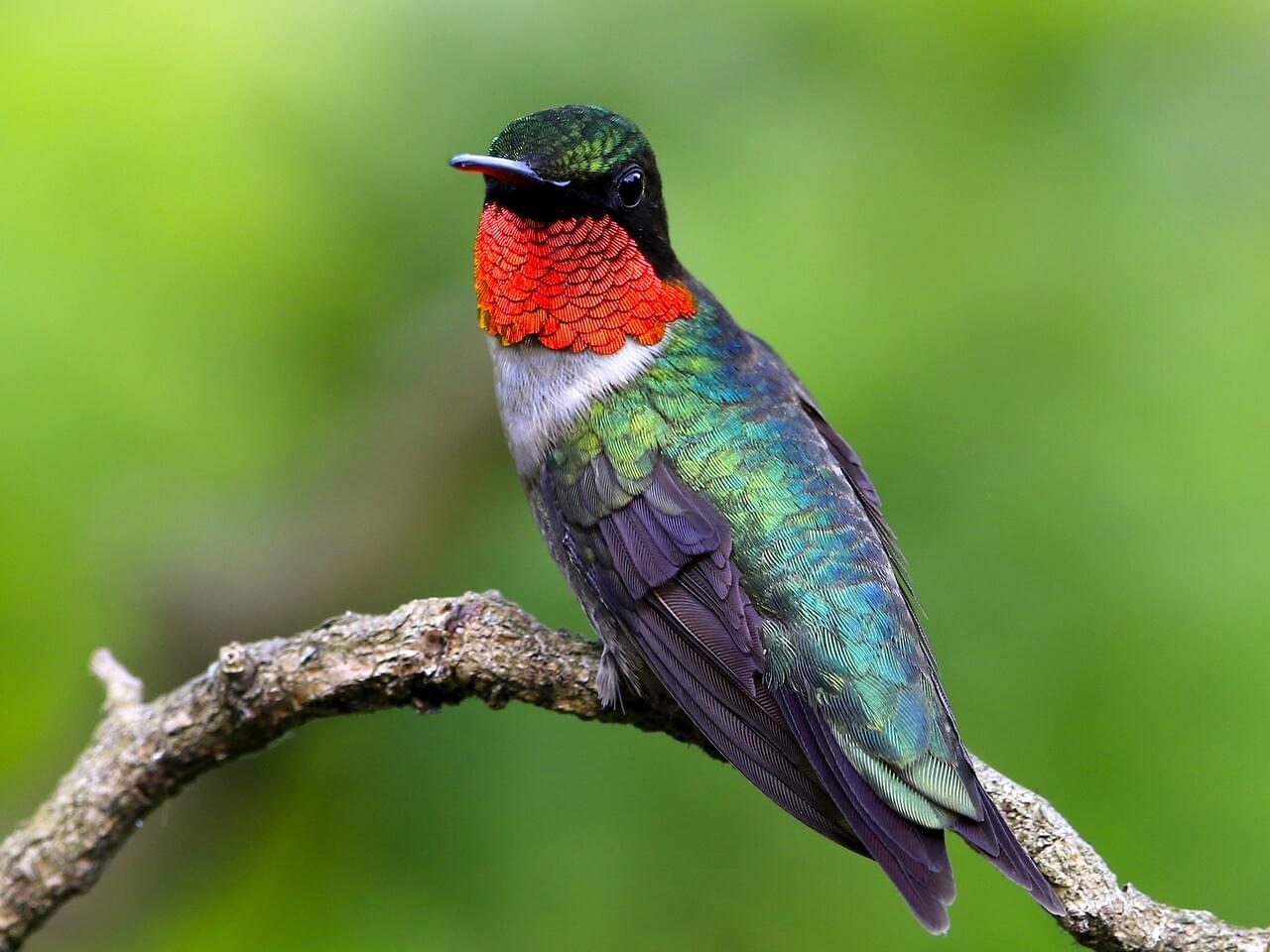
Appearance

Typical Sound
© Randolph Little / Macaulay Library
Size & Shape
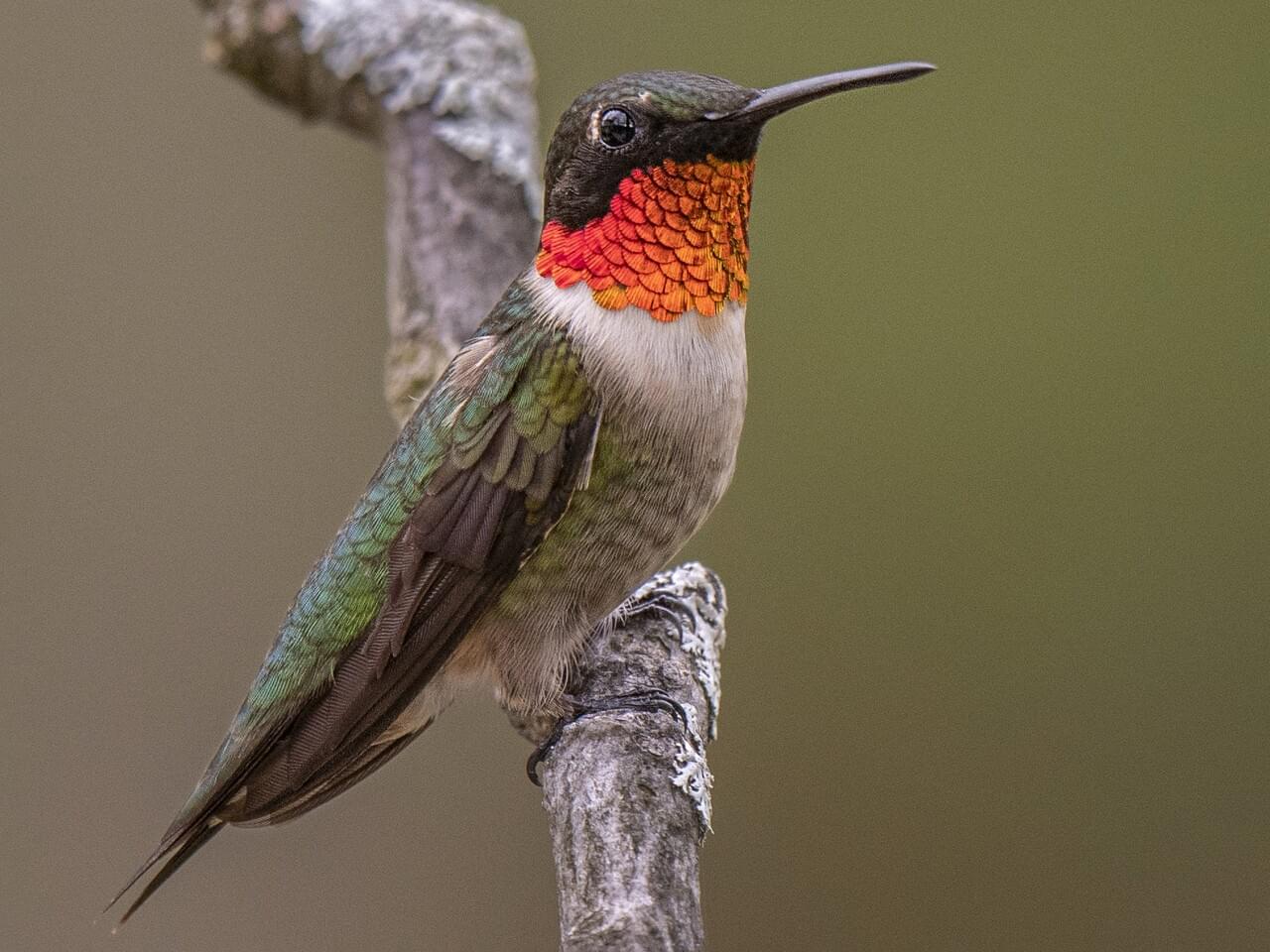
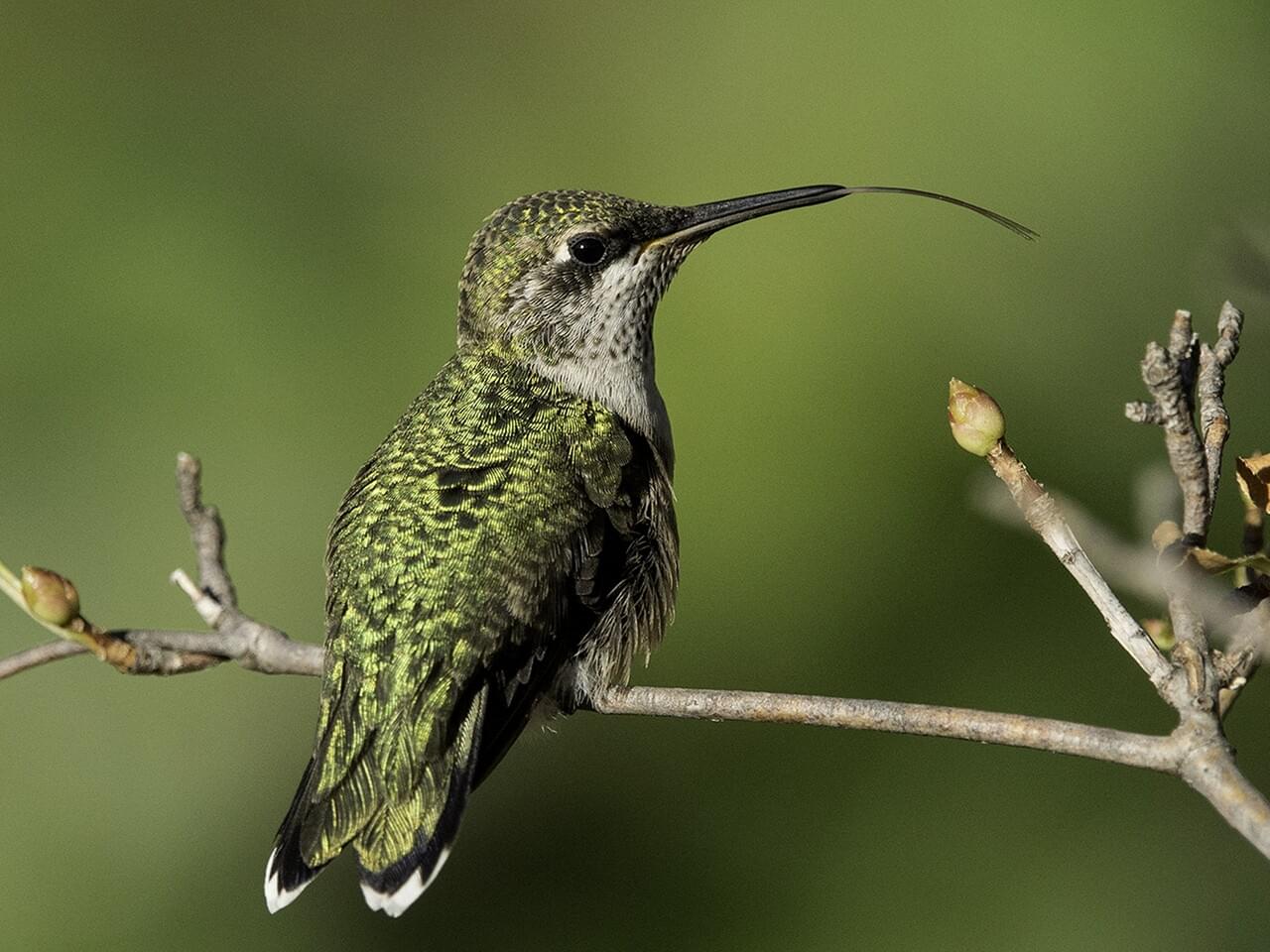
The Ruby-throated Hummingbird is a small hummingbird with a slender, slightly downcurved bill and fairly short wings that don’t reach all the way to the tail when the bird is sitting.
Color Pattern
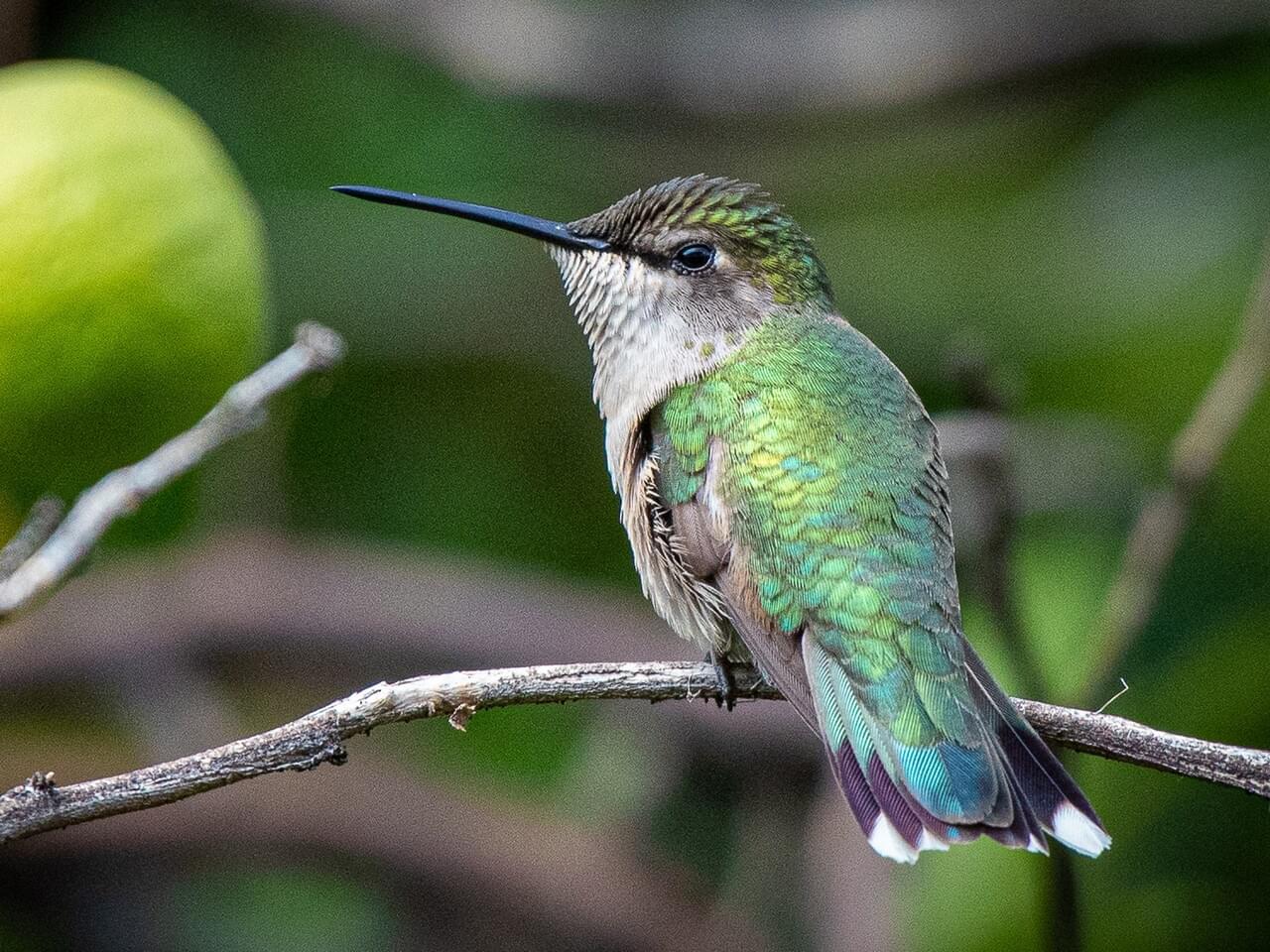
Ruby-throated Hummingbirds are bright emerald or golden-green on the back and crown, with gray-white underparts. Males have a brilliant iridescent red throat that looks dark when it’s not in good light.
Behavior
Ruby-throated Hummingbirds fly straight and fast but can stop instantly, hover, and adjust their position up, down, or backwards with exquisite control. They often visit hummingbird feeders and tube-shaped flowers and defend these food sources against others. You may also see them plucking tiny insects from the air or from spider webs.
Habitat
Ruby-throated Hummingbirds live in open woodlands, forest edges, meadows, grasslands, and in parks, gardens, and backyards.
Migration
Medium to long-distance migrant. Most Ruby-throated Hummingbirds spend the winter in Central America, and most get there by flying across the Gulf of Mexico. Some birds stay in North America along the Gulf Coast, parts of the southern Atlantic coast, and at the tip of Florida; these are usually birds from farther north rather than birds that spent the summer there.
Plumage Photos
Similar Species
Ruby-throated Hummingbirds don't overlap in range with other hummingbirds except the Black-chinned in central Texas (although other species do regularly turn up in eastern North America). Male Black-chinned Hummingbirds have a black throat with a purple-iridescent strip at the base. Male Anna's Hummingbirds have glittering red foreheads. Broad-tailed Hummingbirds (males and females) have buffy flanks and rufous patches in the tail. Rufous Hummingbirds (males and females) have orange-rufous flanks and in the tail. Many female hummingbirds are very difficult to tell apart, particularly in flight when you can't get a good look at them. Female Black-chinned Hummingbirds have longer wings that reach the tip of the tail or go slightly beyond it. They also have flight feathers that widen slightly at the tip, giving each feather a slightly bulbous, club-shaped look. These species only overlap slightly in central and southern Texas.
- The Ruby-throated Hummingbird beats its wings about 53 times a second.
- The extremely short legs of the Ruby-throated Hummingbird prevent it from walking or hopping. The best it can do is shuffle along a perch. Nevertheless, it scratches its head and neck by raising its foot up and over its wing.
- Scientists place hummingbirds and swifts in the same taxonomic order, the Apodiformes. The name means “without feet,” which is certainly how these birds look most of the time.
- Ruby-throated Hummingbirds prefer to feed on red or orange flowers (though it's not necessary to color the sugar water you put in a hummingbird feeder). Like many birds, hummingbirds have good color vision and can see into the ultraviolet spectrum, which humans can’t see.
- Ruby-throated Hummingbirds normally place their nest on a branch of a deciduous or coniferous tree; however, these birds are accustomed to human habitation and have been known to nest on loops of chain, wire, and extension cords.
- Ruby-throated Hummingbirds are eastern North America’s only breeding hummingbird. But in terms of area, this species occupies the largest breeding range of any North American hummingbird.
- Male Ruby-throated Hummingbirds don’t stick around long. Pairs are together long enough for courtship and mating – just a matter of days to weeks. Then he’s off on his own, and may begin migration by early August.
- The oldest known Ruby-throated Hummingbird was 9 years 1 month old.









