Broad-Billed Hummingbird
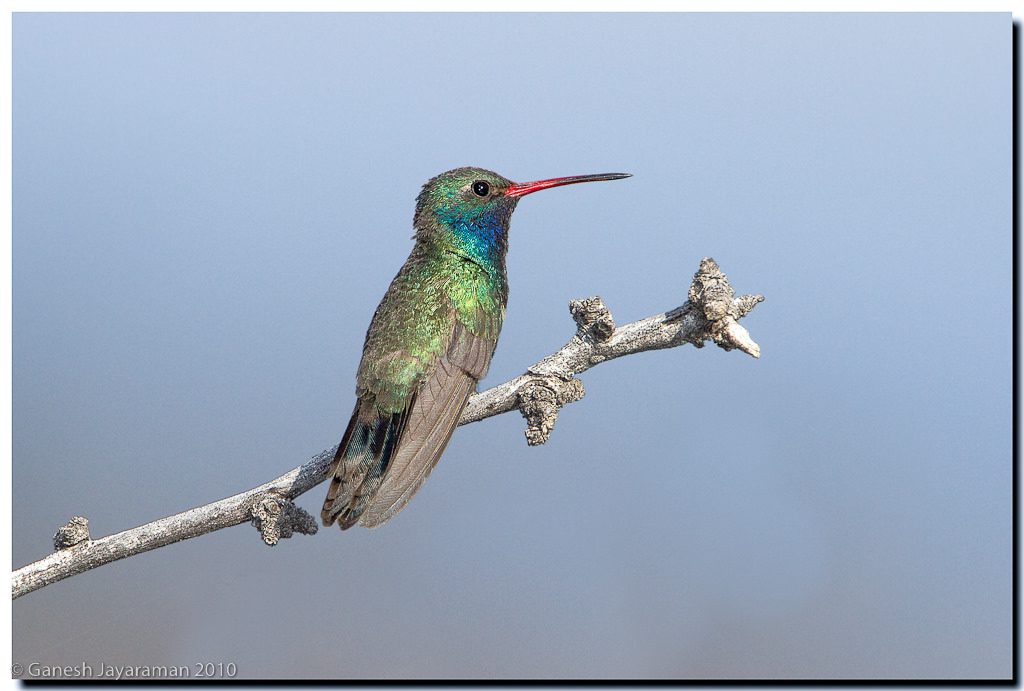
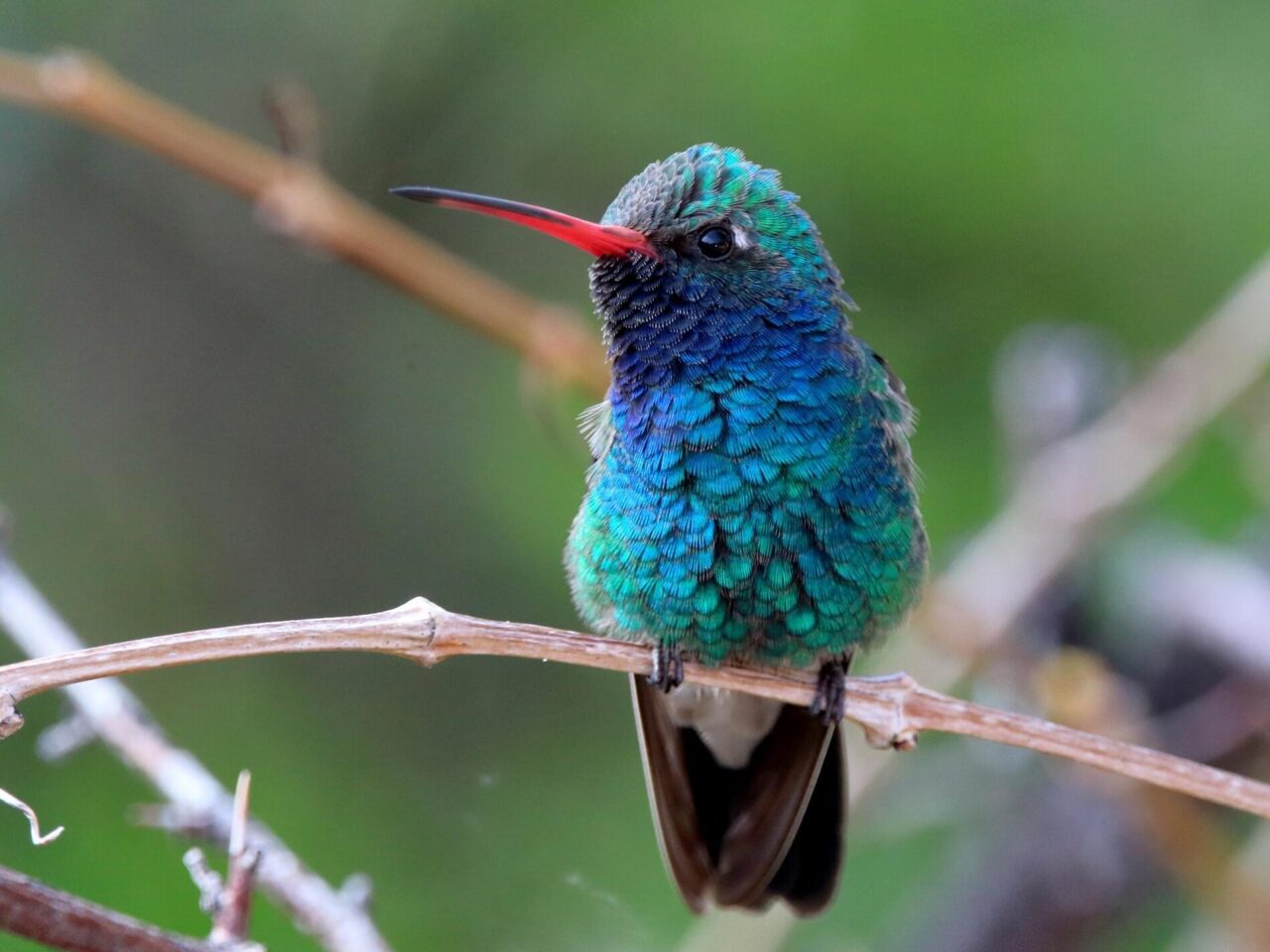
The Broad-billed Hummingbird is a beauty in a beautiful family. The male’s vivid red bill, emerald body, and glittering sapphire throat sets it apart from other U.S. hummingbirds. Most of this species’ range lies in Mexico, but it reaches the mountainous canyons of the southwestern U.S. during the breeding season. There it brightens shady, flower-filled ravines and residential gardens, and is a frequent visitor to hummingbird feeders. In courting the female, the male makes a precision flight display likened to a hypnotist’s swinging pocket watch.

General Information
Range
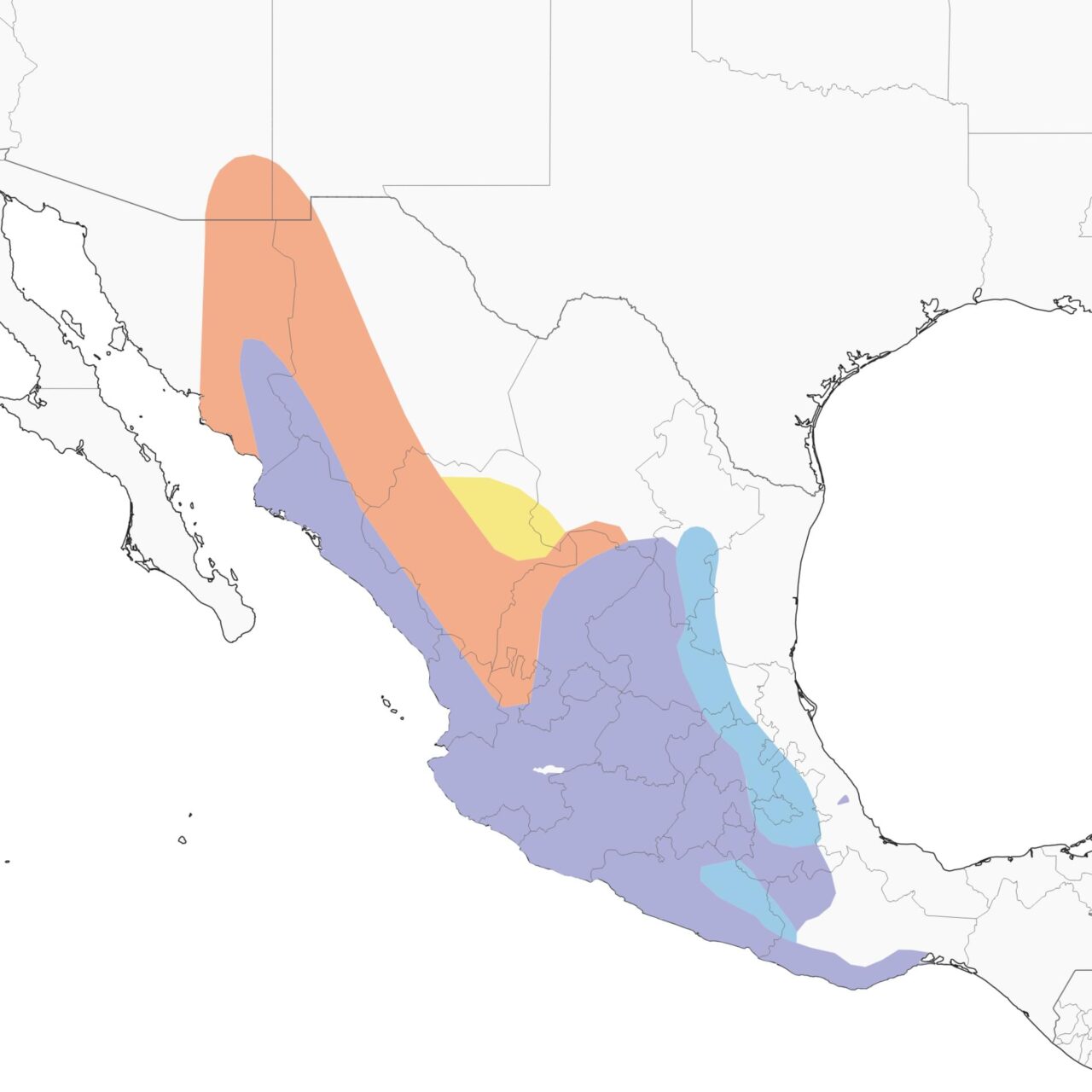
Habitat
In the United States, Broad-billed Hummingbirds nest mostly along streams in canyons, usually below 6,500 feet elevation. They forage in canyons and mountain meadows as high as 9,800 feet, especially in summer after the monsoonal rains cause flowers to bloom en masse. In Mexico, the species frequents many habitat types, from lowland thorn forests and wetter tropical deciduous forests up into mountain canyons. In the United States, key plant species for Broad-billed include Arizona sycamore, Fremont cottonwood, desert willow, seepwillow, willow groundsel, burro brush, honey mesquite, whitethorn acacia, red barberry, netleaf hackberry, one-seed juniper, Arizona white oak, gray oak, soapberry, graythorn, woolly buckthorn, littleleaf sumac, and ocotillo, as well as different species of agave.
Food
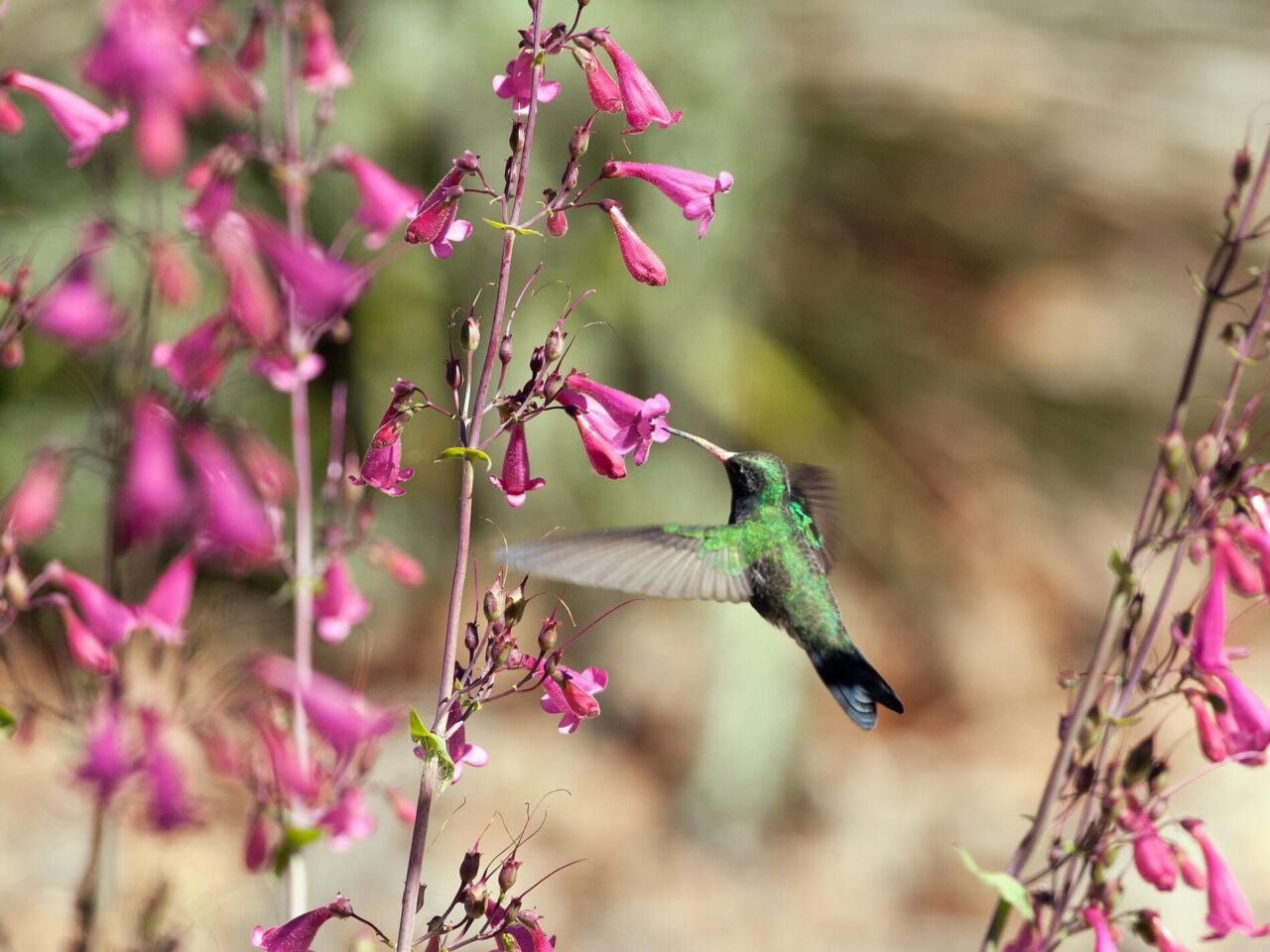
It feeds on nectar by hovering at flowers, and insects by hawking in mid-air.
Behavior
It occurs from the southwestern United States, where birds are summer visitors, south through western Mexico to the Isthmus of Tehuantepec. Its breeding is timed to coincide with the peak flowering season in a given area.
Nesting
The female builds a nest in a protected location in a shrub or tree. Females lay two white eggs.
How to Identify
Appearance

Adult Description
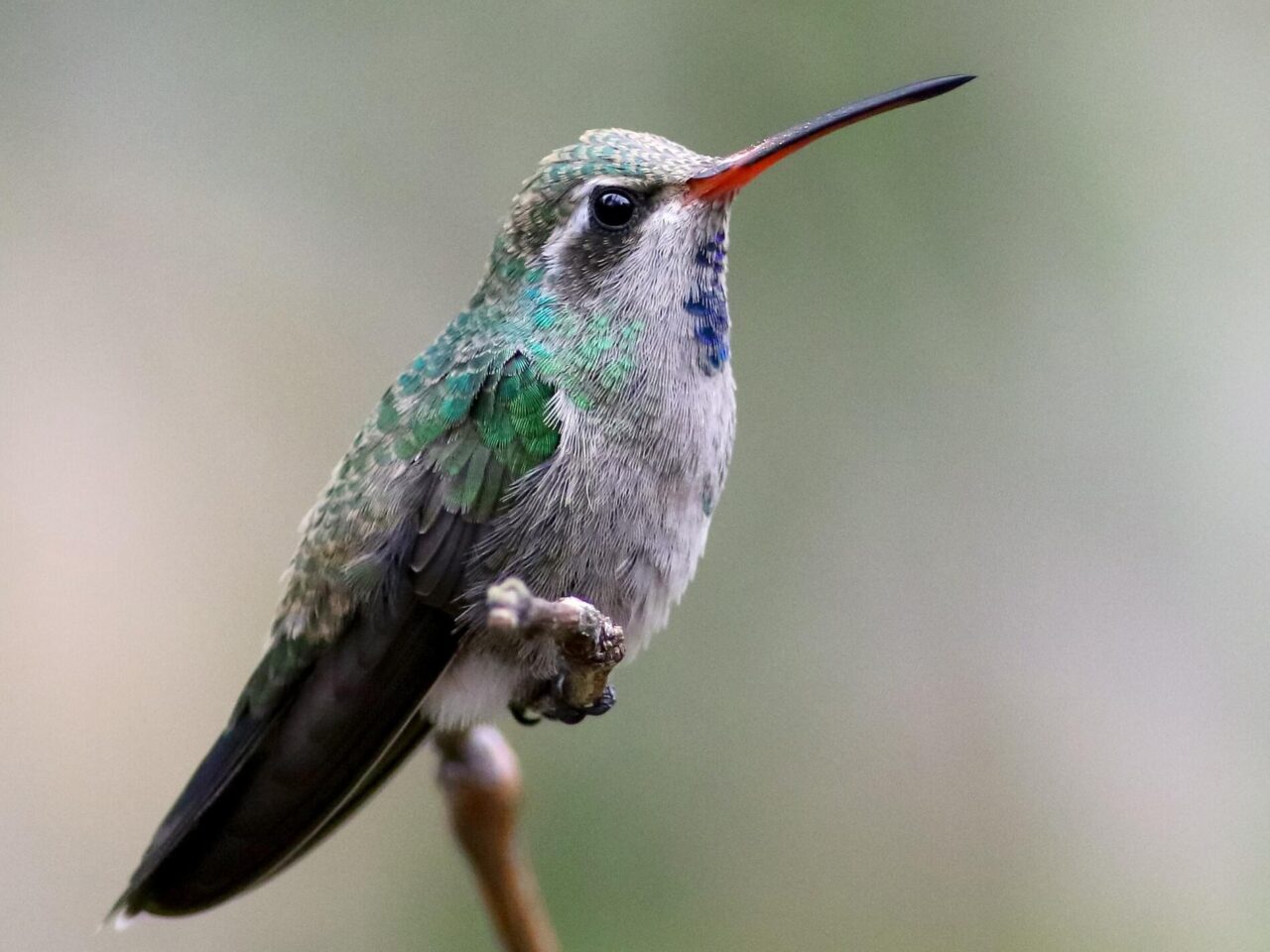
Small hummingbird. Broad, notched tail. Long, red bill with dark tip. Green back. Male with blue throat and green chest. Female with white line over eye, dark ear-patch, and gray underparts.
Immature Description
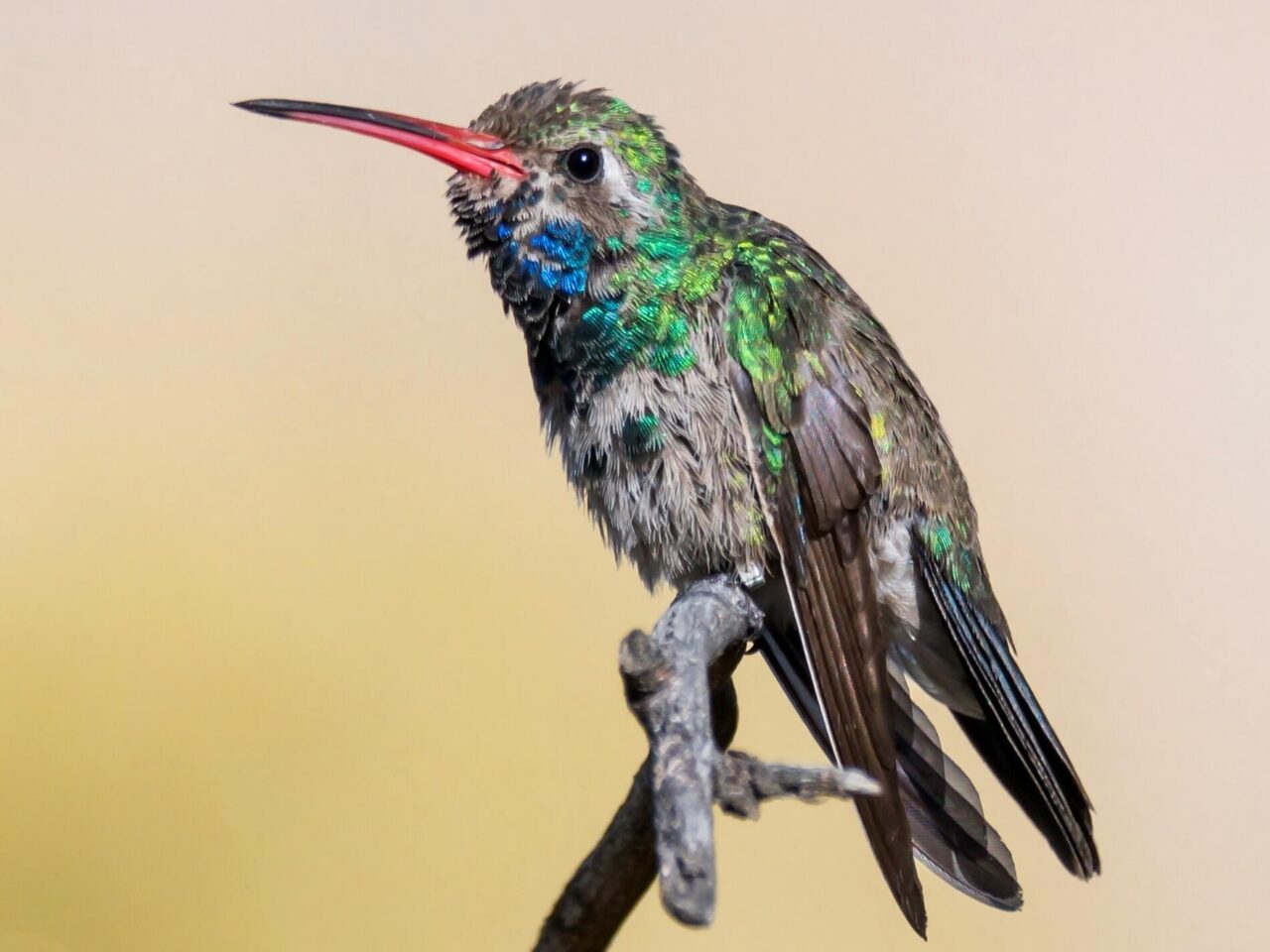
The juveniles look similar to the female adults; immature males have blue and green grow patchy feathers on the throat area.
Plumage Photos
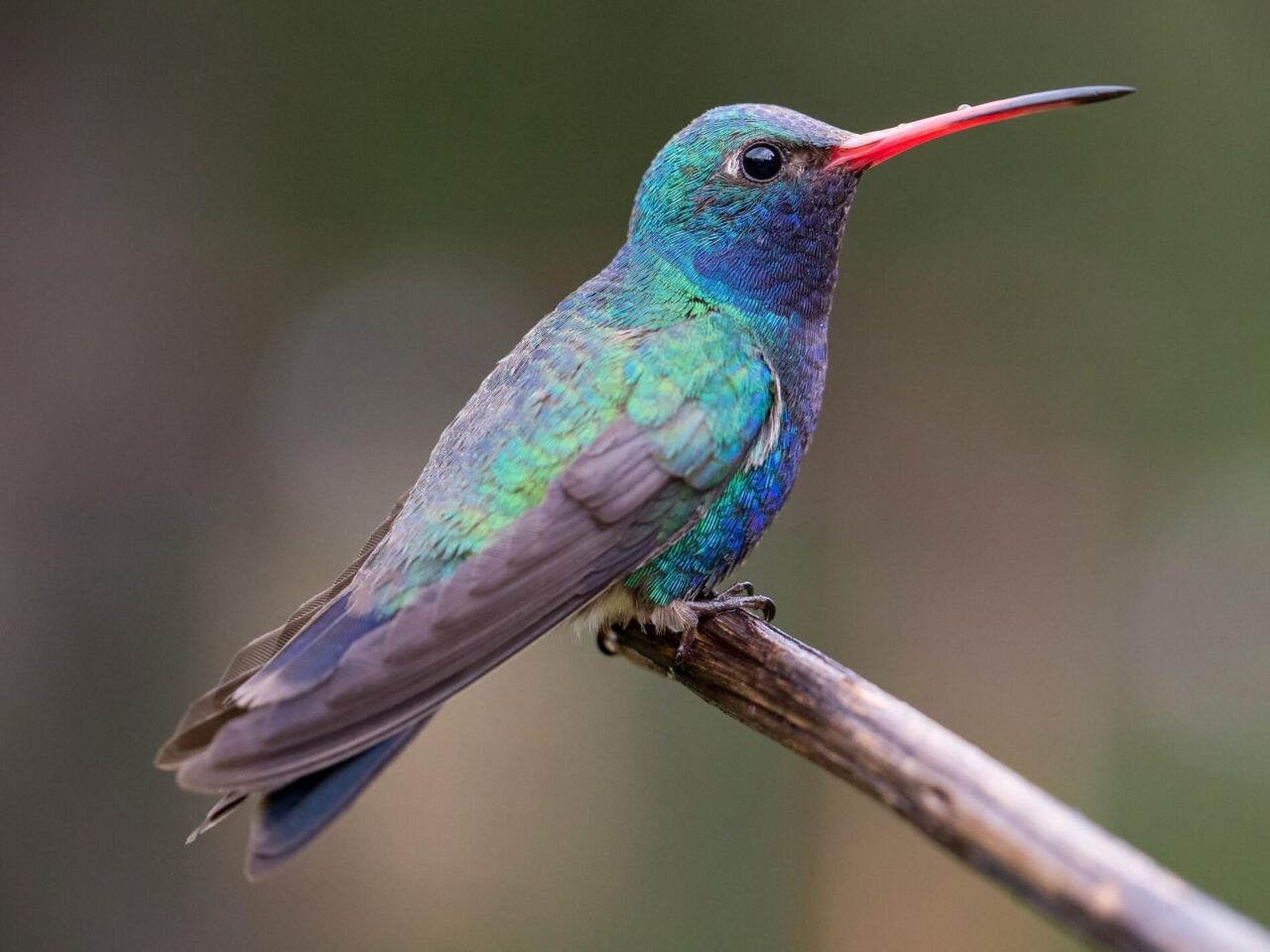

© Ryan Sanderson / Macaulay Library
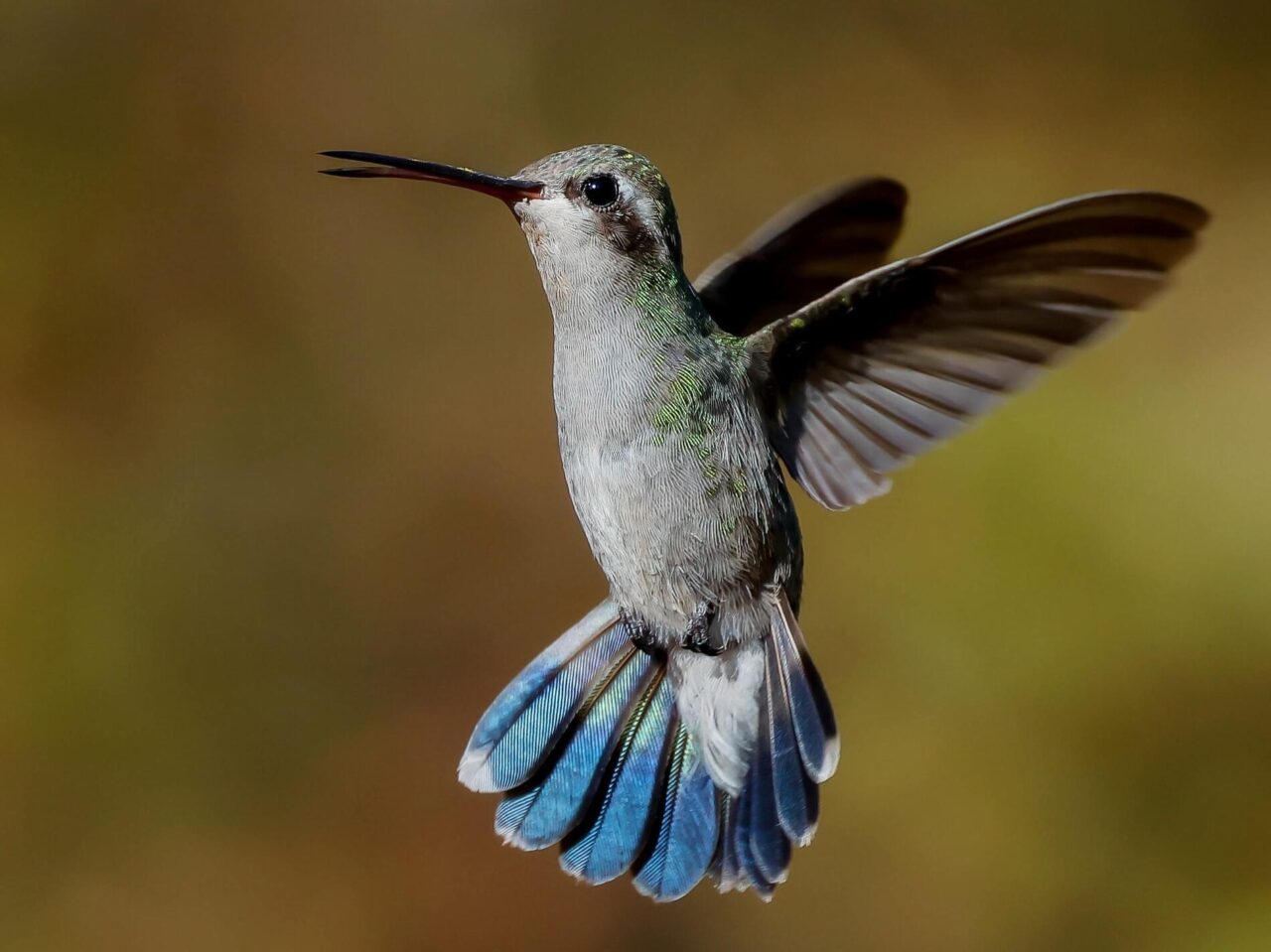

© Fernando Ortega / Macaulay Library

© Spencer Follett / Macaulay Library

© Jim Merritt / Macaulay Library

© Max Nootbaar / Macaulay Library

© Jay McGowan / Macaulay Library

© Jessie Barry / Macaulay Library
Similar Species
Juvenile and adult female Broad-Billed Hummingbirds closely resembles juvenile and adult female White-Eared Hummingbird. Broad-Billed Hummingbird’s ear patch is grayish, while White-Eared’s is blackish. Center of Broad-billed’s throat is clear gray, while White-eared’s throat is spotted.
Fun Facts
Did you know?!
- Like other hummingbirds, the Broad-billed Hummingbird probably consumes about 1.6 to 1.7 times its body weight in nectar each day.
- The male Broad-billed Hummingbird performs a courtship display, starting by hovering about a foot from the female and then flying in repeated arcs, like a pendulum.